Table of Contents
- Understanding the Core of Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview
- The Evolution of Healthcare: From Traditional Practices to Modern Innovations
- Key Components of an Effective Healthcare System: An In-Depth Analysis
- The Role of Technology in Transforming Healthcare Delivery
- Practical Strategies for Improving Healthcare Access and Quality
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
Understanding the Core of Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview
At its core, healthcare is an intricate system designed to promote, maintain, and restore health through the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. This multifaceted industry is built on various elements crucial to its operation and sustainability. Among these are providers and facilities that deliver care, administrative and regulatory bodies that set standards, and the innovative technologies that keep it moving forward. It functions as an ecosystem where roles are dynamic yet interconnected, striving to balance quality, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness for patients and providers alike.
Key Components of Healthcare:
- Providers: This includes everyone from physicians and nurses to allied health professionals like therapists and lab technicians, all working jointly to offer comprehensive care.
- Healthcare Facilities: These range from hospitals and clinics to specialized care centers and home healthcare services, providing various levels of care and expertise.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations such as telehealth, electronic health records, and diagnostic devices continually reshape how care is accessed and delivered.
In understanding the depth of healthcare, it’s vital to consider the pivotal role of policies and financial frameworks that govern it. This sector thrives on funding models and insurance systems designed to make care accessible while managing expenses. Below is a simplified table illustrating some healthcare funding mechanisms:
| Funding Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Public Funding | Government programs like Medicare and Medicaid. |
| Private Insurance | Policies provided by private insurers, offering varied coverage. |
| Out-of-Pocket | Direct payments by individuals for services received. |
These elements collectively form the backbone of healthcare, ensuring that it functions efficiently while adapting to the evolving needs of the population it serves.


The Evolution of Healthcare: From Traditional Practices to Modern Innovations
Over centuries, healthcare has transformed from rudimentary practices into a sophisticated interplay of science and technology. In earlier times, healing largely revolved around natural remedies and traditional knowledge. Communities relied on elders and practitioners for guidance on medicinal herbs and spiritual wellness. Rituals and cultural beliefs heavily influenced these methods, aiming to harmonize the body’s balance and energy. Despite their ancient origins, these practices provided foundational knowledge that continues to inspire holistic approaches in contemporary healthcare.
The introduction of scientific inquiry and technological advancement marked a significant shift in medical practices. The Industrial Revolution and subsequent technological innovations brought about the development of modern medical equipment and vaccinations, which have become pillars of today’s healthcare systems. This era saw the inception of healthcare institutions that formalized the study of medicine and vastly improved the accuracy of diagnoses and treatments. Key developments included improved surgical procedures, the discovery of antibiotics, and the ability to perform complex medical analyses using imaging technologies.
Today’s healthcare landscape is defined by rapid advancements in digital health technology. Innovations like telemedicine, artificial intelligence in diagnostics, and personalized medicine are transforming patient care. These technologies emphasize accessibility and efficiency, breaking down geographical barriers to healthcare access and providing tailored solutions to individual health concerns. Other notable advancements include the development of wearable health devices, which empower individuals to monitor their wellness in real-time. This evolution not only reflects an era of unprecedented medical possibilities but also highlights a shift towards patient-centered care, wherein technology complements compassionate, quality service.

Key Components of an Effective Healthcare System: An In-Depth Analysis
The backbone of any effective healthcare framework lies in its capacity to deliver safe, patient-centered services. Accessibility serves as a primary pillar, ensuring that all individuals, regardless of socio-economic status, can receive necessary medical services without encountering financial barriers. This requires a seamless integration of public and private sectors, combining resources to enhance reach and affordability. Additionally, geographic accessibility is crucial, with decentralized facilities and telemedicine becoming indispensable in bridging gaps in underserved areas.
A well-rounded system must emphasize quality in its services, underpinned by a commitment to continual improvement and adherence to evidence-based practices. Quality care is characterized by professionals who are adequately trained, protocols that reflect the latest scientific findings, and mechanisms that promote transparency and accountability. Patient safety, as a subset of quality, focuses on reducing risks of harm associated with care. This includes rigorous infection control measures, standardized procedures, and technologies that prevent medical errors.
Efficiency is essential in managing healthcare resources wisely without sacrificing quality. It involves strategic allocation and utilization of medical and financial resources, ensuring optimal outcomes with minimal waste. The interplay of efficiency with other components is evident in streamlined administrative processes, where reduced paperwork and enhanced digital systems save time and costs. The following table presents a comparative overview of these components:
| Component | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Widespread reach of services | Equitable healthcare for all |
| Quality | High standards, adherence to evidence-based practices | Improved health outcomes |
| Efficiency | Optimal use of resources | Cost-effective care provision |


The Role of Technology in Transforming Healthcare Delivery
In recent years, the evolution of technology has significantly reshaped how medical services are both accessed and delivered, leading to a more personalized and efficient system. Telemedicine stands out as a pivotal change driver, particularly for rural and underserved areas. By utilizing high-speed internet connections and advanced communication tools, patients can now consult healthcare professionals remotely, reducing travel time and making healthcare more accessible. This has been especially beneficial during global health crises, offering safe alternatives to in-person visits without compromising quality.
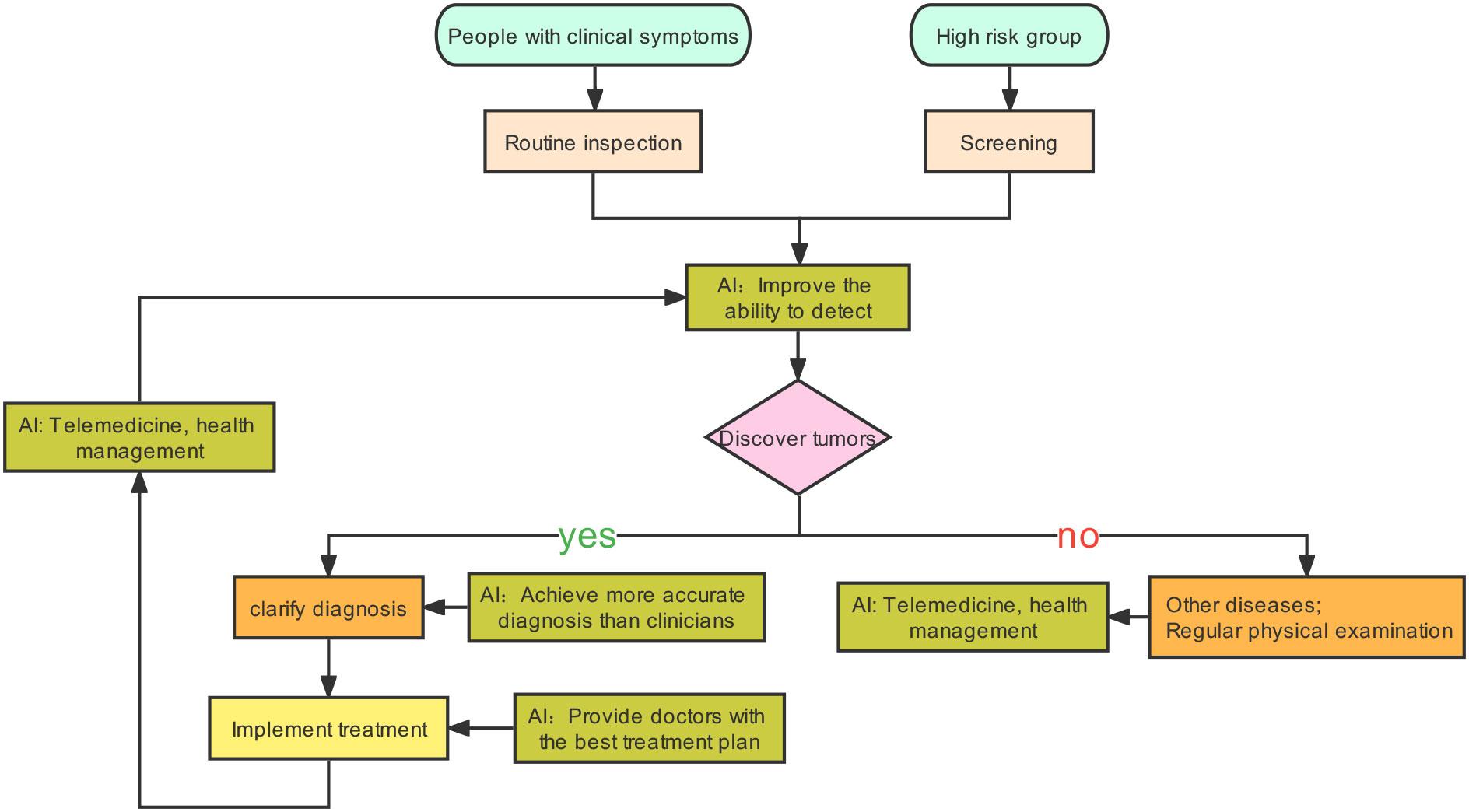
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in diagnostics is transforming patient care. These technologies enable rapid analysis of medical data, from radiological images to genetic sequences, allowing for earlier and more accurate disease detection. As a result, healthcare providers can plan more effective treatment strategies, enhancing patient outcomes. Additionally, these innovations support health professionals by streamlining administrative tasks, freeing up more time for patient interaction and care.
Another transformative aspect is the use of wearable technology and mobile health apps, which empower individuals to take a more active role in managing their health. These tools monitor everything from heart rate to sleep patterns, providing real-time data and insights. Users can set wellness goals, track their progress, and receive personalized health tips. This proactive approach encourages healthier lifestyle choices and aids in early detection of potential health issues, making healthcare a more integrated and continuous experience.

Practical Strategies for Improving Healthcare Access and Quality
Innovative healthcare delivery models are vital to bridging the gap in medical access and improving the quality of care. Community health programs stand out as effective strategies, leveraging local resources to address specific health care deficits. Empowering communities with education and self-management programs significantly benefits chronic disease outcomes. Telehealth services, a burgeoning segment within healthcare, extend the reach of quality medical advice and treatments to remote areas, thus ensuring that geographical challenges do not hinder patient care. Meanwhile, local health partnerships, involving stakeholders such as private companies and government agencies, create synergies that can fund and sustain these initiatives long-term.
Investing in technology is another strategic approach to enhancing healthcare accessibility and service excellence. Digital health records facilitate seamless information transfer between providers, minimizing the lapse between diagnosis and treatment. By promoting interoperability standards across platforms, healthcare providers can ensure streamlined patient management processes. Moreover, AI-driven tools can assist with predictive analytics, identifying at-risk populations swiftly and accurately. This proactive approach enables early intervention, often at a fraction of the cost incurred in later disease stages. Consider the following elements often included in successful tech implementations:
- Integration of electronic health records
- Patient portals allowing virtual communication
- Wearable technology for real-time monitoring
- Data analytics for informed decision-making
Effective policy-making plays a crucial role in overcoming systemic barriers and ensuring equitable healthcare distribution. Governments can implement regulations that promote affordable healthcare services while incentivizing innovation. Expanding Medicare and Medicaid programs can significantly reduce financial barriers for vulnerable populations. Additionally, policy frameworks that support training for the healthcare workforce can improve service delivery by ensuring providers are equipped with the latest knowledge and skills. Below, a comparison shows the potential impacts of strategic policy interventions:
| Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Telehealth policies | Increase in rural patient outreach |
| Subsidies for low-income families | Reduction in healthcare costs |
| Workforce training programs | Improved patient outcomes |




0 Comments